Valves are the pressure regulators used to cut off the flow of a gas or liquid automatically when a certain pressure is achieved.A pressure regulator uses negative feedback from controlled pressure to control the fluid to a desired value. Usually regulators are used to control high pressure supply tanks or lines to reduce the pressure at safe levels for different applications. There are other applications like heat furnace, gas grills and medical equipment where regulators are commonly used. There are a variety of pressure regulators in the market like electronic air regulator. You can buy it according to your needs.
An electronic air regulator, a type of pressure regulator, employs electronic components to precisely control and maintain a desired pressure in a system. It utilizes sensors to measure the pressure and adjusts the opening and closing of valves or other control mechanisms accordingly. Electronic regulators provide accurate and dynamic pressure control, making them suitable for applications requiring tight pressure tolerances. They often offer features like digital displays and programmable settings for extra control and efficiency.
What is a pressure regulator?
A pressure regulator is a valve that uses negative feedback from the regulated pressure to control the pressure of a fluid to a desired value. Regulators are used to control the flow of gasses and liquids. They can be integrated devices with a pressure setting, a restrictor, and a sensor all in one body, or they can be separate pressure sensor, controller, and flow valve.
Regulator is an essential part of pressure setting including a resistor and sensor ,controller and valves.
There are two types of regulator found
- Pressure reducing regulator
- A back pressure regulator
To maintain or control the level of air in a pneumatic system an air pressure regulator is used. Regulators can be used to operate equipment safely, efficiently, and effectively by maintaining a consistent air pressure. An electronic air regulator helps in maintaining the flow of air. The pressure reducing regulator lowers the input pressure to a specified output pressure, ensuring a safe and controlled flow.
Conversely, a back pressure regulator maintains a set pressure at the outlet and controls the pressure upstream. In pneumatic systems, air pressure regulators are crucial for consistent and safe operation, controlling air levels for various equipment. Electronic air regulators offer enhanced precision and automation, aiding in maintaining a steady and optimal airflow in the system.
How does a pressure regulator work?
There are two types of pressure involved inlet and outlet pressure. A pressure regulator reduces a supply (inlet) pressure (which is a higher pressure) to a lower outlet pressure. It maintains its pressure regardless of input pressure and fluctuation in supply. This reduction of pressure is a basic characteristic of a pressure regulator.
If gas is a fluid then the main purpose of the regulator is to match the supply of a gas with respect to demand placed on it. A constant output pressure has to be maintained. Regulator flow should decrease if the load on the system decreases and vice-versa. It is preferable if the controlled pressure does not deviate much from the set point throughout a wide range of flow rates, but it is also good if the flow through the regulator is stable and the regulated pressure does not oscillate excessively.
To keep the outlet pressure at the appropriate set-point, servo electronic pressure regulators (EPRs) use a push valve and a vent valve. To maintain the set-point, a small internal pressure sensor checks the output pressure, and a digital or analog controller changes the timing of the servo valves.
A DC power supply and a set-point signal are normally required for these EPRs. Analog controllers typically accept input of either current (4-20 mA) or voltage (0-10 or 0-5 VDC). In addition to the typical analog standards, models with digital circuits can accept serial communications (such as RS-232 or DeviceNet). Most models also have a feedback signal that informs the pressure sensor’s value.
The operation of a pressure regulator involves a delicate balance between the forces exerted by the fluid or gas and the mechanical components within the regulator. When the pressure at the inlet exceeds the set point, the regulator’s internal mechanism, often a diaphragm or piston, responds to reduce the flow area, thus reducing the pressure downstream. Conversely, if the pressure drops below the set point, the mechanism adjusts to increase the flow area, maintaining the desired outlet pressure. This precise control ensures a steady and safe flow in the system.
Conclusion
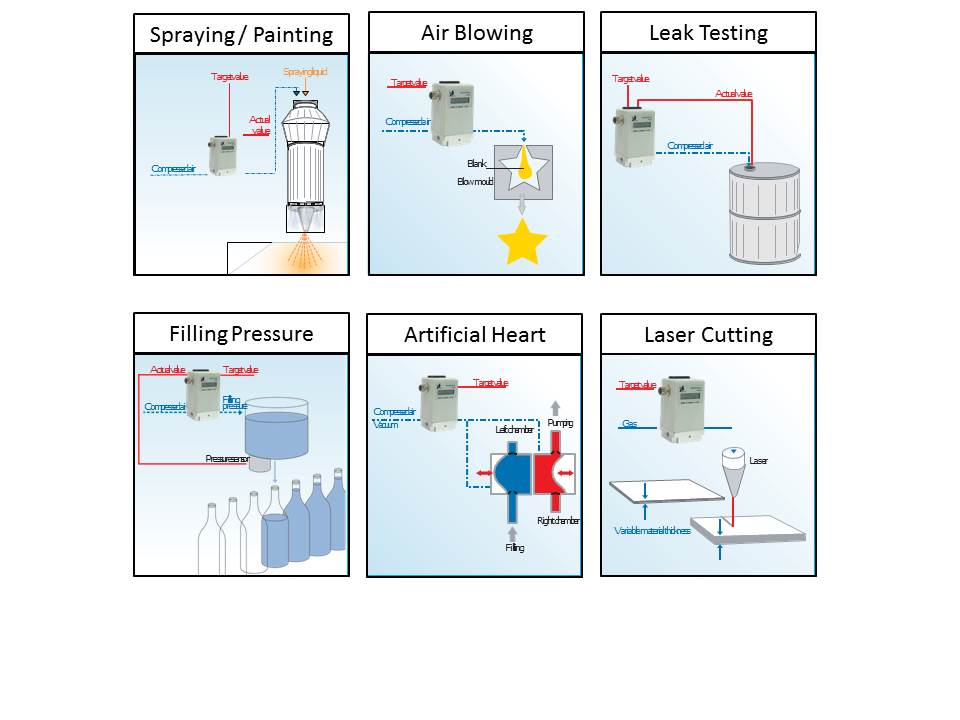
Among different industries and applications, electro pneumatic regulators are commonly used. One of their most common uses is in air compressors, where they are used to regulate the pressure coming out of an air receiver to match what is required for the task. Because corrosive fluids, significant temperature extremes, and high vibration are present in the aerospace industry, pressure regulators play an important role in propulsion pressure management for numerous systems like reaction control systems and altitude control systems.
An electronic air regulator is the latest technology that provides the best control of pressure in a system. In the automotive industry, pressure regulators are pivotal for fuel delivery systems, ensuring a consistent fuel pressure to optimize engine performance and efficiency. Additionally, in manufacturing and industrial processes, these regulators are employed to manage pressures in various pneumatic and hydraulic systems, enhancing overall operational reliability and safety. The medical field utilizes pressure regulators for precise control of gas pressures in equipment like ventilators and anesthesia machines. Moreover, in the oil and gas sector, regulators are fundamental in controlling gas and liquid pressures in drilling operations and transportation pipelines.




